|
ARSENIC
ACID |
|
PRODUCT
IDENTIFICATION
|
| CAS
NO. |
1327-52-2,
7778-39-4 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
231-901-9 |
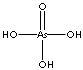
| FORMULA |
AsH3O4 |
| MOL
WT. |
141.94 |
|
HS
CODE
|
2811.29 |
| TOXICITY |
EPA
CODE P010 |
| SYNONYMS |
orthoarsenic acid; Acide arsenique (French); |
| Arsensäure (Dutch); ácido arsenico (Spanish); |
| DESCRIPTION |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
clear
syrupy liquid |
| MELTING POINT |
-35
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
130
C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
2.0 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
16.7 g/100 mL |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
NFPA
RATINGS |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX |
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
wood
treatment, finishing agent for glass and metal,
manufacturing of dyestuffs and organic arsenic compounds, soil
sterilant. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
clear
syrupy liquid |
|
H3AsO4 |
80.0%
min
|
As2O5 |
65.0%
min |
|
As2O3 |
0.1%
max
|
|
HNO3 |
0.1%
max
|
|
Ca
|
0.02%
max
|
|
Fe
|
0.05%
max
|
|
Pb |
0.06%
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
100kgs
in plastic drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
1554
(Solid), 1553 (Liquid)
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
European Hazard Symbols: T, Risk Phrases: 23/25, Safety Phrases: 20/21 |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF ARSENIC AND ITS COMPOUNDS
|
Arsenic is a highly poisonous metallic element in the nitrogen family of group
Va in the periodic table. Symbol As; aomic number 33; atomic mass 74.9216;
melting point ca 817°C; sublimation point ca 613°C; specific gravity 6.80 or
7.004; 5.73; valence -3, 0, +3, or +5.; electronic config. [Ar]3d104s24p3. It
appears in three allotropic forms, yellow, black, and gray. The stable form is
a brittle, steel-gray hexagonal solid that oxidizes rapidly in air, and at high
temperatures burns to form a white cloud of arsenic trioxide. Arsenic and some
arsenic compounds sublime when heated and convert to gaseous form. Arsenic is an
omnipresent element as arsenic minerals in the various lithosphere or fossil
fuels including realgar, orpiment, and arsenopyrite. It is prepared
commercially from arsenical pyrites (sulfide ores) by condensation of sublimed
gas and by the reduction of white arsenic with carbon. This element
contributes hardness and used in preparing alloys for hard and
corrosion-resistant properties. Arsenic is added to germanium to form gallium
arsenide used in the production of semiconductor devices like integrated
circuits and also used in laser and light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to convert
electricity directly into light. Arsenic compounds are used as agricultural
pesticides (such as copper and lead arsenates), wood preservative, for glass
making, in alloys, electronics, in indigo and calico printing, in tanning, in
bronzing and pyrotechnics and in the manufacture of dyestuffs. Though some
organic compounds of arsenic were used in medicine such as Salvarsan, used in
the treatment of syphilis and yaws, Arsenic preparations for medical purpose
are no longer recommended. Arsenate is salt or ester of arsenic acid having a
negative ion of AsO43- , arsenite is a salt or ester of arsenious acid having a
negative ion of AsO43- derived from aqueous solutions of As4O6 and arsenide is a negative, trivalent
binary arsenic compound such as H3As or GaAs.
Many arsenic compounds are strong poisons. Arsenic compounds include:
- Arsenenic acid
(meta-arsenic acid, HAsO3 10102-53-1)
- Arsenenous acid (HAsO2,
13768-07-5)
- Arsenic
Trichloride (AsCl3, CAS#:7784-34-1):
Oily, clear liquid; decomposes in
water; used in ceramics, organic chemical syntheses, and in the preparation of
pharmaceuticals; light sensitive and moisture sensitive.
- Arsenic
Trisulfide (As2S3,
CAS#:1303-33-9): An acidic compound in the form of yellow or red
monoclinic crystals with a melting point at 300°C; occurs as the mineral
orpiment; used as a pigment.
- Arsenic Acid (H3AsO4,
CAS#: 1327-52-2, 7778-39-4): White, poisonous crystals, soluble in water and
alcohol; used
in wood treatment, finishing agent
for glass and metal, manufacturing of dyestuffs and organic arsenic
compounds, soil sterilant. Also known ortho-arsenic acid.
- Arsenic acid monoammonium salt
(AsH6NO4,CAS#:
13462-93-6)
- Arsenic Disulfide (As2S2,
CAS#:1303-32-8): Deep red, lusturous monoclinic crystal ;insoluble in water; used in fireworks; naturally occurs as realgar.
- Arsenic Pentasulfide (As2S5):
Yellow crystals; insoluble in water; readily decompose to the trisulfide and sulfur; used as a pigment.
- Arsenic
Pentoxide: (As2O5,
CAS#:1303-28-2
): white, deliquescent compound that decomposes by heat and is soluble in water.
same application with arsenic trioxide.
- Arsenic Trioxide (As2O3,
CAS#:1327-53-3):
toxic glassy, amorphous lumps or crystal compound;
slightly soluble in water; octahedral crystals
change to the monoclinic form by heating at 200°C; arsenious acid;
occurs naturally as
arsenolite and claudetite; used in some medicinal
preparations but in small quantities. It is produced as a by-product of metal smelting
operations. It has been estimated that 70% of the world arsenic production is
used in timber treatment as copper chrome arsenate, 20% in agricultural
chemicals as arsenic-containing pesticides, and the remainder in glass, pharmaceuticals and non-ferrous alloys.
- Arsenin:
A
heterocyclic organic compound composed of arsenic in six-membered ring structure
in which
the carbon atoms are unsaturated, with no
nitrogen atoms present.
- Arseniosiderite (Ca3Fe4(AsO4)4(OH)4·
4H2O): A yellowish-brown mineral consisting of a basic iron calcium arsenate and
occurring as concretions.
- Arseno Compound:
a compound containing an As-As bond
with the general formula (RAs)n, where R represents a functional group;
structures are cyclic or long-chain polymers.
- Arsenobismite
(Bi2(AsO4)(OH)3): A yellowish-green mineral consisting of a basic
bismuth arsenate and occurring in aggregates.
- Arsenoclasite
(Mn5(AsO4)2(OH)4): A red mineral consisting of a
basic manganese arsenate. Also spelled arsenoklasite.
- Arsenolamprite
(FeAsS): A lead gray mineral consisting of
nearly pure arsenic; occurs in masses with a fibrous foliated structure.
- Arsenolite
(As2O3): A mineral crystallizing in
the isometric system and usually occurring as a white bloom or crust. Also known
as arsenic bloom.
- Arsenopyrite
(FeAsS): A
white to steel-gray mineral crystallizing in the monoclinic system with
pseudo-orthorhombic symmetry because of twinning; occurs in crystalline rock and
is the principal ore of arsenic. Also known as mispickel.
- Arsine
(H3As):
A colorless, highly poisonous gas with an unpleasant odor.
- Arsinic Acid
( R2AsO2H):
derived from trivalent arsenic; an example is cacodylic acid, or dimethylarsinic
acid, (CH3)2AsO2H.
- Arsanilic acid
(98-50-0): 4-Aminophenylarsonic Acid derived from orthoarsenic acid, is an
arsenical antibacterial veterinary medicine used in the prevention and the
treatment of swine dysentery.
- Arsonic Acid:
An acid derived from orthoarsenic acid, OAs(OH)3; the type formula is
generally considered to be RAsO(OH)2; an example is para-aminobenzenearsonic
acid, NH2C6H4AsO(OH)2.
- Arsonium (AsH4): A radical which may be considered analogous to the ammonium
radical in that a compound such as AsH4OH may form.
- Arsphenamine (139-93-5)
- Calcium Arsenate (Ca3(AsO4)2,
CAS #: 7778-44-1)
- Carbarsone
(121-59-5)
- Copper arsenate (As2Cu3O8,
CAS#: 10103-61-4)
- Cupric Arsenide (CuHAsO3,
CAS #: 10290-12-7)
- Dimethylarsine ((CH3)2AsH, 593-57-7)
- Gallium Arsenide (AsGa,
CAS #: 1303-00-0)
- Lead Arsenate
(PbHAsO4,
CAS #: 7784-40-9)
- Magnesium arsenate (As2Mg3O8,
CAS #: 10103-50-1)
- Manganese arsenate
(AsHMnO4,
CAS #: 7784-38-5)
- Methylarsine (CH3AsH2, 593-52-2)
-
3-Nitro-4-hydroxy-phenyl arsonic acid
(121-19-7) : Also called Roxarsone;
used in veterinary medicine
to promote growth, feed efficiency and pigmentation
and to control swine dysentery. . It
is used as a synergist of primary anticoccidials.
- 4-Nitrophenylarsonic acid (98-72-6)
- Potassium Arsenate (KH2AsO4,
CAS #: 7784-41-0)
- Potassium Arsenite (KH(AsO2)2,
CAS #: 10124-50-2)
- Sodium
Arsenate (Na3AsO4,
CAS #: 7631-89-2,
7778-43-0(Dibasic), 13464-38-5(tribasic))
- Sodium
Arsenite (NaAsO2,
CAS #: 7784-46-5)
- Trimethylarsine ((CH3)3As,
593-88-4)
- Tryparsamide (554-72-3)
- Zinc Arsenate (As2O8Zn3,
CAS#:13464-44-3)
|
|
